 User Guide — Record Access Restriction
User Guide — Record Access Restriction
To restrict and track access to sensitive charts such as those belonging to employees, VIP patients, or other patients needing additional privacy protections, you can apply a "record access restriction" privacy protection note.
Note: This privacy protection note was previously called "block patient."
Once a record access restriction is applied to a patient's record, there are three access types for that record: a free access user, a restricted record access user, and a no access user.
-
A free access user is the rendering, scheduling, or supervising provider assigned to an appointment for a patient with a record access restriction. The free access user can access the patient’s record for 15 days before and after the appointment.
This user does not require the Privacy: Access Blocked Patients or Emergency Access: Privacy: Access Blocked Patients permission. However, if a provider will need access to any patients with a record access restriction, we recommend granting them one of these permissions in case they are not the rendering, scheduling, or supervising provider, or they need to access a record outside the window of 15 days before or after the appointment.
Changes to the rendering, scheduling, or supervising provider for an appointment immediately affect user access. For example, if the scheduling provider is changed from Provider A to Provider B, Provider A is no longer a free access user, and Provider B immediately becomes a free access user.
-
A restricted record access user is someone who is not the rendering, scheduling, or supervising provider, but requires access to the record of a patient with a record access restriction. This user must have either the Privacy: Access Blocked Patients or Emergency Access: Privacy: Access Blocked Patients permission. When accessing the record, a restricted record access user must provide a reason for the access and can access the record for only 12 hours. If the user attempts to access the record after 12 hours, they must again provide a reason for the access.
-
A no access user is someone who is not a free access user or a restricted record access user, and therefore cannot access the record of a patient with a record access restriction. If this user attempts to access a record with a record access restriction, either a Forbidden page or a pop-up window displays to indicate that they are not able to access the record. If this user requires access, they must be granted either the Privacy: Access Blocked Patients or Emergency Access: Privacy: Access Blocked Patients permission.
A Record Access Restriction Activity report provides visibility into who accessed patient records that have a record access restriction privacy protection note.
Note:
Patients can request record restriction using the Record Restriction option within Patient Portal secure messaging. They are provided with the following information:
"A Record Restriction allows you to withhold your health information from one or more individuals or entities. To request a record restriction, include the name of the individual or entity in the message field below. Please note, we are not required to fulfill your request if it could affect your care."
After a patient sends a restriction request, a patient case is created. This patient case then enters the Clinical Inbox, within the Portal row. From there, your staff can take action to restrict the record access accordingly.
Restricted record access users require either the Privacy: Access Blocked Patients or Emergency Access: Privacy: Access Blocked Patients permission.
To access reports on the Clinicals tab of the Report Library, you must have the Clinicals user permission and the Report: Report Library: Clinicals permission. The Report: Report Library: Clinicals permission is included in the following roles:
- Practice Superuser role
- Report Reader role
-
Access a patient’s Privacy Information page using one of the following options:
-
On the Quickview, click Manage Privacy (under the Privacy heading)
-
On the Check-in page, click Manage Privacy (under the Privacy heading)
-
On the Patient Actions Bar, click Registration, and then click Privacy Information
-
-
Under Privacy Notes at the bottom of the page, click the record access restriction link.
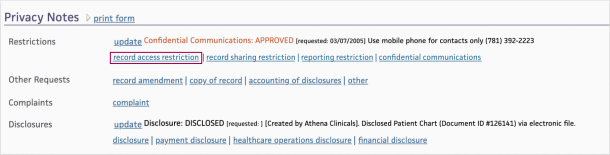
The Privacy Protection Notes page appears. -
Source — Select the person who requested the “record access restriction” privacy protection note.
-
Form — Select the form that was used for the request, if applicable.
-
Request Date — Verify, enter, or select the date the request was made (usually the current date).
-
Review Date — If you are authorized to approve or deny patient privacy requests (requires the Privacy: Approve Patient Restrictions permission), enter or select the date that you reviewed this request.
-
Status
If you don’t have the Privacy: Approve Patient Restrictions permission, verify that the status of the request is set to REVIEW. The request will need to be reviewed by a user with the Privacy: Approve Patient Restrictions permission.
If you have the Privacy: Approve Patient Restrictions permission, you can create and approve a restriction yourself by setting the status to APPROVED. You can also select the status to approve or deny restriction requests made by other users.
Note: Only record access restrictions in APPROVED status will cause a record to be restricted.
Note: Approved privacy restriction notes appear on the View Appointment Ticklers page under the Patient Notes column.
-
Request Note — Enter a description of the request. If you want this note to appear on the window that requires users to enter a reason for accessing the restricted record, select Show on the "Record Access Restriction" modal. If this check box is selected, up to 150 characters of this note will appear on the modal window.
-
Review Note — If you are authorized to approve or deny patient privacy requests, enter any notes about reviewing this request. If you want this note to appear on the window that requires users to enter a reason for accessing the restricted record, select Show on the "Record Access Restriction" modal. If this check box is selected, up to 150 characters of this note will appear on the modal window.
If the Show on the "Record Access Restriction" modal check box is selected for both the Request Note and the Review Note, both notes appear on the modal window and the Request Note appears first.
-
Click Save. The patient's Quickview page appears, with the number of privacy notes in REVIEW status updated. The new request also appears on the Privacy Information page under the Privacy Notes heading.
See Privacy Protection Notes for more instructions about this page.
The difference between privacy protection notes is:
-
“Record access restriction” restricts user access to patient records. Only users with Privacy: Access Blocked Patients or the Emergency Access: Privacy: Access Blocked Patients permissions can access charts that have this privacy protection, or the user must be a rendering, scheduling, or supervising provider for the patient. A rendering, scheduling, or supervising provider for an appointment can access a restricted patient’s record for 15 days before and after the appointment without specific permissions.
-
"Record sharing restriction" prevents sharing of a patient’s records with other people. For example, a patient can request that their medical information be withheld from a spouse or other family member.
-
"Reporting restriction" excludes a patient from report results when you run reports using the Report Builder. No reports will include a restricted patient unless you select the Show Reporting Restricted Patients option when running the report.
-
“Confidential communications” requests an alternative means or alternative location for communicating a patient’s health information. For example, a patient might request that you use a cell phone number instead of a home phone number to communicate medical information.
- Display the Report Library: On the Main Menu, click Reports. Under General, click Report Library.
- Click the Clinicals tab.
- Click run next to Record Access Restriction Activity in the Standard Reports section of the tab.
The Run Report: Record Access Restriction Activity page appears. -
Select the criteria for the report:
-
From date - To date — Enter the start and end dates for the report or select a range from the drop-down menu.
Note: You must apply at least one type of date filter.
- Accessing User — Leave the default to view access of restricted patient records by all users, or click Selected and search for and select specific users to include in the report.
- Patient by ID — Leave the default value ALL to view access of all records with a record access restriction, enter a specific patient's ID, or enter a list of patient IDs separated by commas.
- Report Format — Select the format for your report results.
- HTML table — Display the report results on your screen.
- Text (tab-delimited) — Export the report results to a .csv file in tab-delimited format.
- Text (comma-delimited) — Export the report results to a .csv file in comma-delimited format.
- Report Options — Select report options.
- Suppress Column Headings — Select this option to remove column headings from the report results.
- Suppress Report Name — Select this option to remove the report name from the report results.
- Show Filter Criteria — Select this option to include your selected filter criteria in the report results.
- Run Offline (will appear in your Report Inbox tomorrow morning) — Select this option for very long reports. Reports that are run offline appear in your Report Inbox the morning after the request.
-
-
Click Run Report.
If a restricted record access user (not the rendering, scheduling, or supervising provider) attempts to access a restricted access patient record in athenaOne, a modal window displays, and the user must select a reason for access before continuing. After providing a reason for access, the user can access the patient’s record for 12 hours.
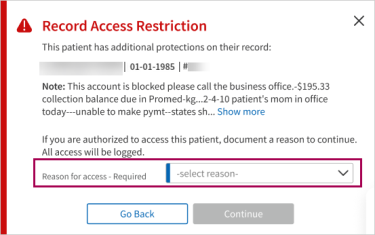
Note: When creating a record access restriction, you can optionally enter Request and Review notes that appear on this modal window below the patient information.
If the user selects “Other," the user must also manually enter a specific reason for access.
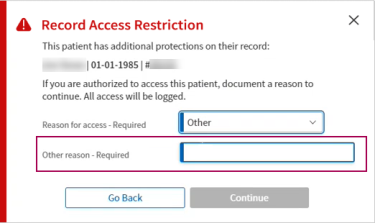
Note:
This pop-up window currently displays only when you attempt to access any of the following pages for a patient with a record access restriction. Workflows not listed here still use the old blocked patient functionality and will be updated in a future release.
-
Appointments
-
Billing Summary
-
Charge Entry
-
Chart
-
Check-In
-
Check-Out
-
Claim History
-
Clinical Inbox: list view, grid view tasks, and flagged tasks
-
CPI View
-
Encounter
-
Patient Account View
-
Patient Search
-
Post Payment
-
Quickview
-
Registration
-
Schedule
When the “block patient” (now “record access restriction”) privacy protection note was applied to a patient record, only users with the Privacy: Access Blocked Patients or Emergency Access: Privacy: Access Blocked Patients permission could previously view information about the patient, such as the patient's chart, documents, and information like name, photo, age, date of birth, phone number, etc. These permissions were not patient-specific; users with this permission could access any patient record that had a record access restriction.
Users without the Privacy: Access Blocked Patients or Emergency Access: Privacy: Access Blocked Patients permission could not perform clinical documentation, check-in, checkout, charge entry, and other common functions for patients that had a record access restriction.
Note: We are applying changes gradually across athenaOne, so you will continue to see this previous privacy protection behavior in some workflows.
Identifying information of patients with a record access restriction is redacted across athenaOne according to the type of access that the user has.
-
For free access users, no patient identifying information is hidden.
-
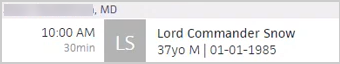
For restricted record access users, the patient’s first name and MRN are displayed, and all other identifying information is hidden. The following examples show how patients with a record access restriction appear in the Patient Search and Schedule to a restricted record access user in athenaOne.


Once a restricted record access user enters a reason for access, they can see the full name, DOB and gender. Last note, action note, and appointment note remain hidden. The following examples show how the same patients with a record access restriction appear in the Patient Search and Schedule after the user enters a reason for access.
Note: The
 to the left of the patient name in Patient Search indicates a patient with a record access restriction.
to the left of the patient name in Patient Search indicates a patient with a record access restriction.
-
For no access users, all patient identifying information is hidden. The following example shows how a patient with a record access restriction appears to a no access user in the Schedule.

In Patient Search, no information of a restricted access patient is displayed in the results grid. Instead, if any restricted access patients are found in the search, the number of additional (restricted access) patients found is displayed above the results grid.
Each time a restricted record is accessed, the access is logged, and information about the access can be displayed in the Record Access Restriction Activity Report.
For more information about the report, see Record Access Restriction Activity Report.
-
Dr. Smith, a provider at Seven Hills Medical Group, is scheduled as the rendering provider for a patient who has a record access restriction privacy protection note.
-
Within 15 days of the appointment, he is able to access the patient’s record, complete clinical documentation, and complete other functions as necessary.
-
If he needs to access the patient’s record more than 15 days before or after the appointment, he can do so as a restricted access user if he has the Privacy: Access Blocked Patients or Emergency Access: Privacy: Access Blocked Patients permission.
-
Jane, a front desk staff at Seven Hills Medical Group, needs to check in and update the insurance information for a patient who has a record access restriction privacy protection note.
-
As a user with the Privacy: Access Blocked Patients permission, she is able to see the patient’s first name on the schedule.
-
When she clicks the check in button, a modal window asks for her reason for access.
-
She selects a reason and clicks Continue.
-
She is able to complete the check in and update the patient’s registration as usual.
-
Matthew, a front desk staff at Seven Hills Medical Group, needs to update the insurance information for a patient who has a record access restriction patient privacy protection note.
-
As a user without the Privacy: Access Blocked Patients or Emergency Access: Privacy: Access Blocked Patients permission, he is unable to find the patient in Patient Search or see any of the patient’s information on the schedule.
-
He must contact his supervisor to get either the Privacy: Access Blocked Patients or Emergency Access: Privacy: Access Blocked Patients permission before he can gain access to the patient’s record.